What is in this procedure?
- The legislative requirement for hazard management.
- How to practically identify hazards, assess risks, and systematically control risks.
- Who is responsible for managing and resolving hazards in the workplace?
Who needs to take action?
- Any employee who has identified a hazard.
- All levels of management are directly responsible for assessing and controlling identified hazards and risks.
- Operations Manager
- Site Supervisors
Information you need to know
“Hazard”: refers to a source of danger or something with the potential to cause injury, illness or disease in the workplace. Hazards may be physical, biological, chemical, mechanical and psychological.
“Risk”: is the probability that a hazard, incident or event will cause harm. The Shineline Risk Assessment Matrix is used to determine a risk score, which allocates a risk level of ‘very low risk’, ‘low risk’, ‘moderate risk’ or ‘high risk’.
“Workplace”: means a place, whether in a building or structure, where employees work.
“Hierarchy of Risk Control”: refers to the process used to identify practical measures for eliminating or reducing the risk of incident, injury, illness and disease in the workplace. It works on a top-down approach, with elimination at the top of the hierarchy being the most reliable way to manage the risk, and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) at the bottom of the hierarchy being the least reliable way to manage the risk.
1. Roles and Responsibilities
1.1 Shineline
- Shineline is responsible for having hazard management processes in place that eliminate or reduce the risk of incidents and injuries so far as reasonably practicable.
- Shineline is responsible for ensuring that support and resources are provided to enable effective management of hazards and risks.
1.2 Operational Managers
- Operational Managers are responsible for the following: Ensuring the sites maintains a Hazard Register to record all hazards identified in the workplace.
- Investigating all Incident/Injury/Near Miss Report Forms to identify any underlying hazards.
- Providing assistance in conducting a Risk Assessment, determining appropriate risk control measures and completing the Hazard Register.
- Tabling the Hazard Register at the monthly meetings to enable all staff
members to be aware of the identified hazards on site and any risk
control measures planned.
1.3 Employees
- Employees are responsible for the following: Identifying health and safety issues and reporting them to their immediate Operational Managers / Site Supervisors.
- Completing the relevant processes with the assistance of the Operational Manager, Completing by entering the details in the Hazard Register if the issue relates to an identified hazard.
- Notifying the relevant authority (where applicable, i.e. corporate office,
industrial premises, body corporate or shopping center management) for identified hazards.
2. Hazard Management Process
Hazard Management involves having a systematic process for the identification of hazards, assessment, and control of risk. It includes the following 4 steps:
- Hazard Identification
- Risk Assessment
- Risk Control
- Risk Review
2.1 See the Hazard (Hazard Identification)
Operations Managers shall maintain a Hazard Register and to record all hazards identified at the site and needs to bring those unresolved hazards into monthly meeting discussion forum. Hazards are identified by, but not limited to, the following methods:
- Through observation.
- By talking to employees.
- By completion of the General OHS Inspection Checklist.
- By completion of a Manual Handling Review and Plan.
- By completion of a Manual Handling Risk Assessment.
- By completion of the Hazardous Substances and Dangerous Goods
Checklist.
2.2 Assess the Risk (Risk Assessment)
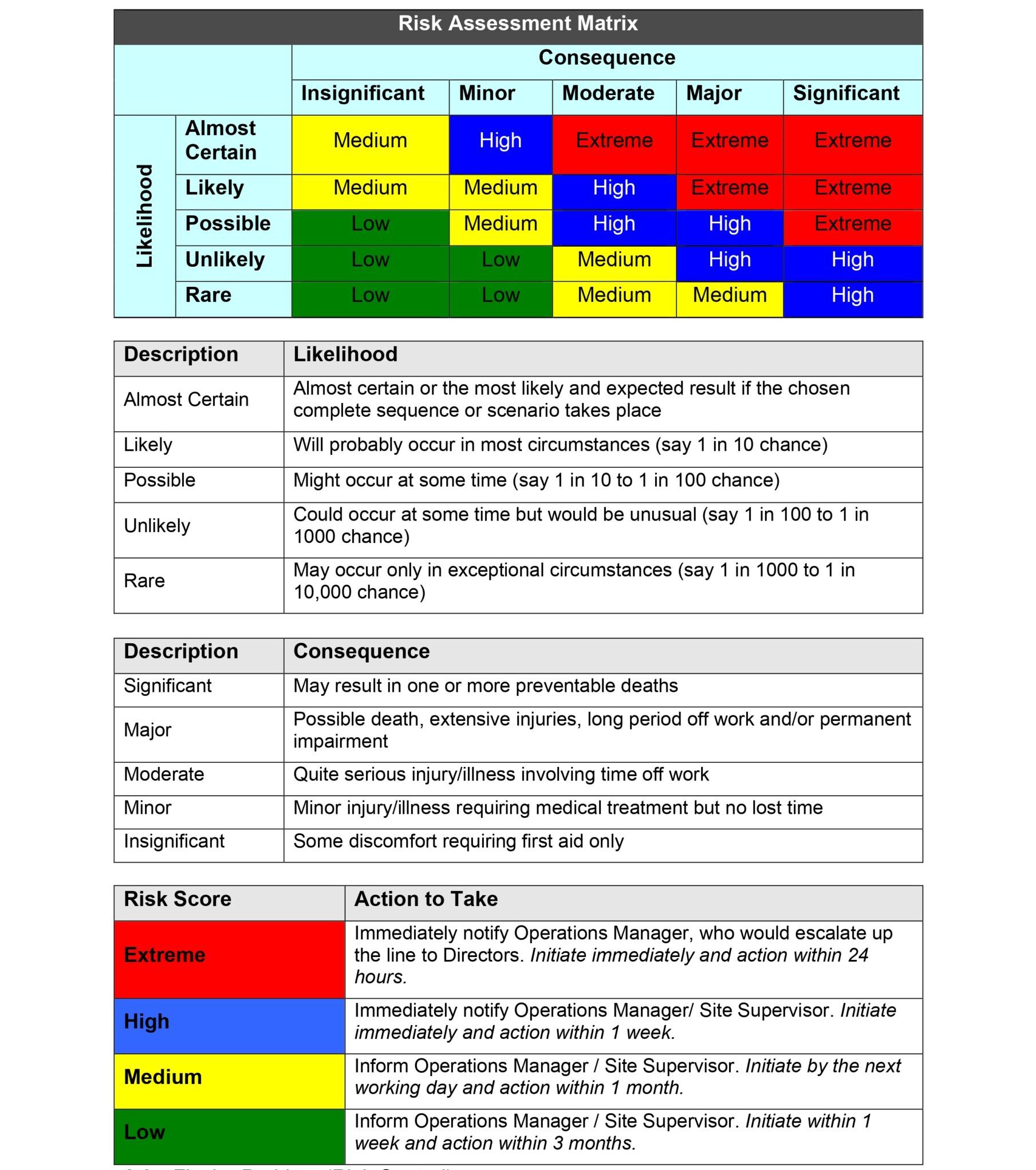
- Conduct a risk assessment for each identified hazard using the Risk Assessment Matrix
- Determine a Risk Score and record in the Hazard Register (complete column ‘Risk Score’).
- Determine the risk score by considering the most likely outcome. Consider the following questions: “How likely could the hazard hurt someone?” and “How badly could someone be hurt?”
- Complete a Risk Assessment in consultation with the site supervisor, Line Manager, persons exposed to the hazard, and employees reporting the hazard.
2.3 Fix the Problem (Risk Control)
- Implement appropriate risk control measures to fix the problem.
- Discuss appropriate risk control options with the site supervisor / Operations Manager, persons exposed to the hazard/risk and employee reporting the hazard/risk.
- Record details in the Hazard Register.
- Allocate a person responsible and timeframe for implementing the risk control(s) and record in the Hazard Register (complete columns ‘Anticipated
Date of Completion’ and ‘Person Responsible’). - Once the risk control measure for the hazard has been completed, record in the Hazard Register (complete column ‘Date Completed’).
- The Hazard Register is a working document, must be accessible to all staff and should not be archived.
2.4 Hierarchy of Risk Control
- Control the risk by using the Hierarchy of Risk Control: Eliminate the hazard, e.g. can you remove the faulty equipment or repair the broken door?
- Substitute the hazard, e.g. can heavy items be replaced with lighter items above shoulder height?
- Engineer/redesign the hazard, e.g. erect barriers around a hole in an access path, use mechanical aids to reduce manual handling.
- Administration, e.g. can employees be made aware of hazards through training, procedures or posters?
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), e.g. can gloves, aprons or goggles be worn to reduce contact with hazards?
2.5 Timeframes for Actioning Risk Control Measures
Once a hazard has been assigned a risk score, the risk control measure must be actioned within the following timeframes:
- Extreme Risk control measures initiated immediately and actioned within 24 hours;
- High Risk control measures initiated immediately and actioned within 1 week, Medium Risk control measures initiated on the next working day and actioned within one month;
- Low Risk control measures were initiated within 1 week and actioned within 3 months.
2.6 Evaluate the Outcome (Risk Review)
Following the implementation of a risk control measure, an evaluation must be completed to ensure the risk control measure has adequately eliminated or reduced the risk. Consider the following:
- Is the chosen risk control measure working effectively? Discuss with staff members involved.
- Have any new hazards been introduced? For example, a step-ladder
reduces the need to over-stretch for high shelves, but introduces a falls
hazard. - Has the residual risk level been reduced? Conduct a further risk assessment to determine if the risk score has been reduced.
3. This procedure will be reviewed in two years from the effective date.
4. Related documents
4.1 Internal
- Hazard Register
- Incident/Injury/Near Miss Report Form
- Manual Handling